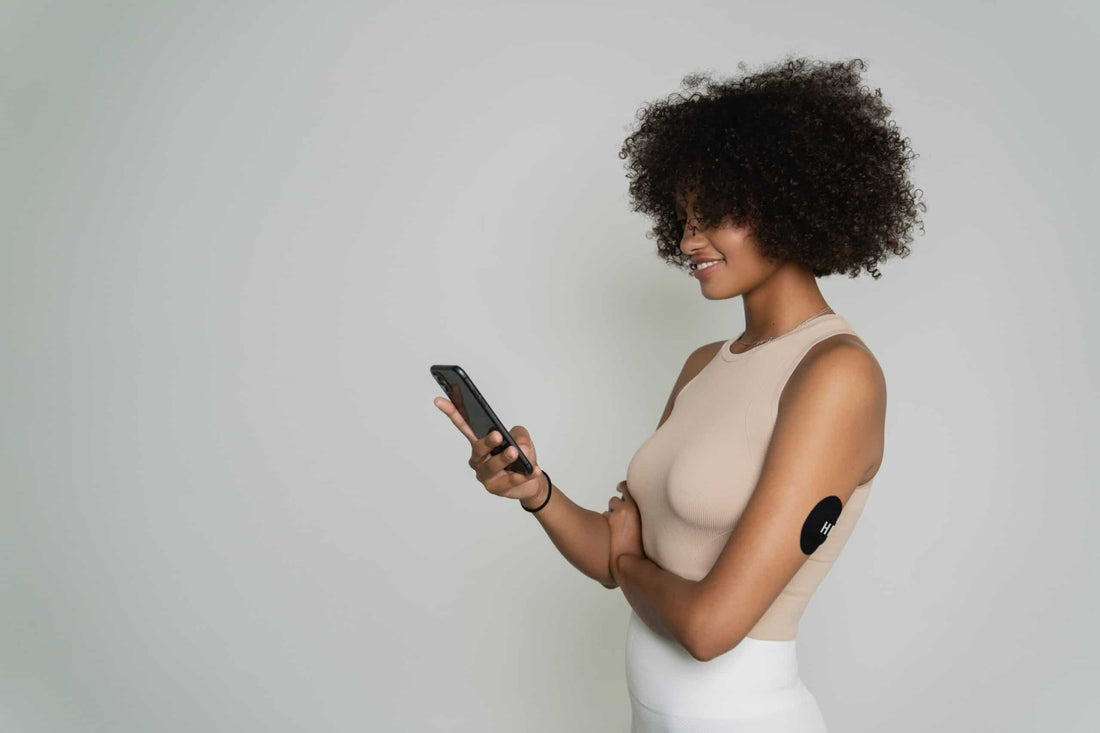
There seems to be no obvious connection between skin, inflammation and blood sugar. However, they are closely linked, as blood sugar influences inflammation, which in turn can affect the appearance of the skin.
It may surprise you, but did you know that the skin is the largest organ in the body?
The outer layer of the skin, the epidermis, is constantly changing and replacing dead or damaged cells.
This layer is important for the human body as it protects it from various factors such as bacteria and chemicals. So we can say without a doubt that healthy skin is very important.
Many lifestyle and dietary factors affect skin health and influence the risk of certain skin diseases. An unhealthy diet can promote inflammation and the onset of certain skin diseases such as dermatitis, acne or psoriasis. Even though these diseases are clinically very different, they have a chronic inflammatory background. Therefore, let us first explain some of the basics of inflammation.
What is inflammation?
Although it causes unpleasant side effects, inflammation is actually a good and healthy response of our immune system to a foreign invader. Inflammation becomes harmful when it persists and begins to damage healthy cells, creating a pro-inflammatory state.
In this context, proper nutrition can suppress the inflammatory response and reduce inflammation.
So what should you eat to reduce inflammation?
The key is to eat a variety of anti-inflammatory foods rather than focusing on one or two specific foods or nutrients. Ideally, your diet should include a combination of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, nuts, seeds, legumes, red wine, fish, and olive oil.
The modern Western diet, which is characterized by high levels of processed foods rich in saturated fats, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars, has been shown to promote inflammation. This is not desirable and should therefore be a smaller part of your diet.
What does that have to do with your blood sugar?
Recently, elevated blood sugar has been shown to contribute to inflammation. The mechanism is complex, but simply put, high blood sugar can lead to the formation of free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that lack an electron. To stabilize their own structures, they "steal" an electron from neighboring molecules, which then damages surrounding tissues, such as skin, and leads to chronic inflammation.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels can improve your skin health. By using it as a real-time tool to adjust your lifestyle and reduce inflammatory processes.